The Working Principles of Brake Master Cylinder and Brake Slave Cylinder
When it comes to the braking system of a vehicle, two important components that work together are the brake master cylinder and the brake slave cylinder. Understanding their working principles is crucial for ensuring optimal braking performance and safety.
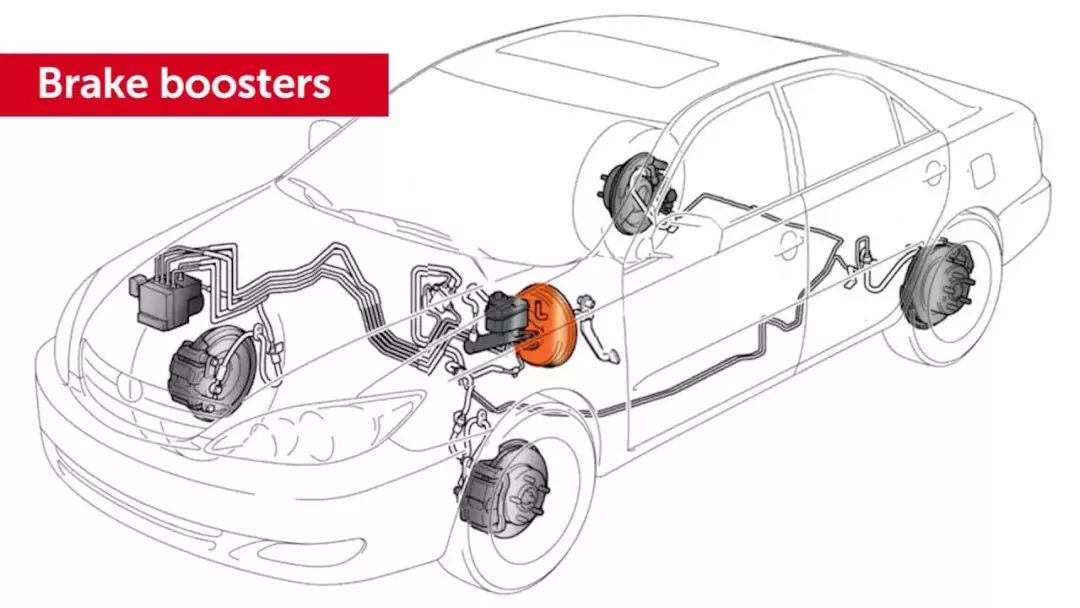
The brake master cylinder, also known as the brake pump, is responsible for generating hydraulic pressure in the braking system. When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, a piston inside the master cylinder is pushed forward, forcing brake fluid through the brake lines. This creates hydraulic pressure that is transmitted to the brake slave cylinders.
The brake slave cylinders, also known as brake calipers or wheel cylinders, are located at each wheel and are responsible for applying the necessary force to stop the vehicle. When hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder reaches the slave cylinders, it causes pistons inside the slave cylinders to move, pushing the brake pads or shoes against the brake rotors or drums. This friction between the brake components creates the necessary stopping force.
It is important to note that the brake master cylinder and slave cylinders work in a closed hydraulic system. This means that any loss of brake fluid or air in the system can significantly affect braking performance. Regular maintenance, including checking brake fluid levels and bleeding the brake system, is essential to ensure proper functioning of these components.
In conclusion, the brake master cylinder and brake slave cylinders are integral parts of the vehicle’s braking system. Understanding their working principles and ensuring proper maintenance is crucial for optimal braking performance and, most importantly, the safety of the driver and passengers.